Posture, etiology of a syndromePaolo
Platania
|
Posturology
guidelines and
interdisciplinary case study |
||||||
|
|
|
|
Posturology
|
The case study
|
The backstage
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evidence of vagally mediated relationship between tongue weakness and posture asymmetry: lineaments and etiology of the postural disorder, a case study. Paolo Platania (2008)
| THREAT CONDITION 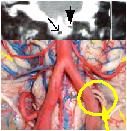 |
THREAT ONSET  |
EMERGENCY STRATEGY  |
STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION  |
IMPLEMENTATION DRAWBACKS (evidences and symptoms of postural disorder) |
||||||||||||||
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Posture science enhancement pays for the present settlement of medical scientific society, this study proposes a different approach and explains the evidences yielded. CASE REPORT: an adult white male lamenting chronic unilateral motor disorder has been submitted to a long and thorough evaluation process by means of a method designed to fully exploit patient’s collaboration and underwent intermediate non invasive therapeutic attempts for differential diagnosis exclusion; final analysis highlights Tongue Motor Insufficiency (TMI), owed to nerve entrapment, as pathogenetic factor of the claimed symptoms as well as of a wider symptomatic picture hereby baptized platania’s syndrome. DISCUSSION: According to the observations, platania’s syndrome is the result of a permanent unilateral muscular spasm aimed at Cranio-Cervical Extension (CCE) and promoted by three actions: 1) main promoter is respiration, triggering Upper Airway Patency Maintenance Reflex (UAPMR) due to unilateral airflow augmented resistance, 2) Head Flexion Insufficiency (HFI) induced by extrinsic tongue muscles weakness and 3) Mandible Retrusion (MR), induced by teeth conflicts, further increasing airflow resistance due to tongue backward motion. Common pathogenesis of all three actions is TMI and the neurogenic etiology is Hypoglossal Rootlets Emergence Entrapment (HREE) under vertebral artery slightly deviated left branch. The complex mechanics, pathomechanics and etiopathogenesis are discussed along with their evidences and further validated by an accurate protocol. CONCLUSION: the theorized cause-effect relationship between “HREE / TMI / UAPMR-HFI-MR / CCE / head and neck posture / body posture / postural syndrome” along with it’s etiopathogenetic factor, not only explains platania’s syndrome, but, since observation and existing literature confirm this conditions to be as diffuse as overlooked, suggests a broad appliance to this theory.
Method
The case is exposed according to the following model:
- Abstract: brief description;
- Method: resources, tools and process;
- Completion status: case workflow description, current completion status and activity in process;
- Platania's syndrome: relationship model of the pathology development;
- Dossier: case elements collection;
- Evidences: case relevant findings;
- Mechanics: case findings relationship analysis and strategy identification;
- Pathomechanics: link between mechanics and pathology;
- Etiopathogenesis: diagnostic process;
- Therapy: therapeutic process;
- Discussion: comprehensive explanation;
- Conclusion: final conclusions;
| METHOD: process | |
| Activity | Description |
| Self evaluation activity | Monitoring all motor/static actions during the whole day. Activities monitored:
|
| Recording activity | Tracing the following daily details in digital format
|
| Retrospective analysis activity | Data analysis aimed at the following:
|
| Literature research activity | Carried out either with
“punctual” approach (to deepen the current
hypothesis) and with a “inspiration” approach (to
advance new hypothesis), resources are:
|
| Diagnostic activity | Aimed to confirm/exclude theories of the
moment, carried out by:
|
| Therapeutic attempts activity | Therapeutic attempts carried out in the absence
of etiological diagnosis; the initial “random therapeutic
activity” to provide accidental and hopefully resolutive
outcome has been superseded by a more “aimed therapeutic
activity”. Therapeutic approach:
|
Completion status
The research activity started in the year 2000 and the case is still in progress, the completion status specification is compliant to the naming convention in section Posture:(click on the labels to navigate)
| EVIDENCES | MECHANICS | PATHOMECHANICS | ETIOPATHOGENESIS | THERAPY | ||||||||||||||
| Pathological process | Etiological process | |||||||||||||||||
| Collection of every evidence arising from whatever observation method | Postural strategy identification by analysing the evidences | Research of the relationship between the mechanics goal and the evidence that may activate it | Diagnostic process to identify the cause of the pathologic evidence | Procedure to treat the pathology in order to restore health | ||||||||||||||
| Informations and documentation collection involved in all the diagnostic and therapeutic process | ||||||||||||||||||
| Management process | ||||||||||||||||||
| DOSSIER | ||||||||||||||||||
Management process:
| DOSSIER (anamnesis, lamented symptoms….) | in progress (Ddo11, Ddo12) |
Pathological process:
| EVIDENCES (clinical, self evaluated, symptomatic..) | completed |
| MECHANICS (postural strategy identification) | completed |
Etiological process:
| PATHOMECHANICS (first primary pathology identification) | completed |
| PATHOMECHANICS (second primary pathology identification) | completed |
| ETIOPATHOGENESIS (first primary etiological diagnosis) | in progress (Ddo10) |
| ETIOPATHOGENESIS (second primary etiological diagnosis) | completed |
| THERAPY (first primary pathology correction) | to be undertaken |
| THERAPY (second primary pathology correction) | first attempt failed (Eot05), wait |
Platania’s syndrome
The current hypothesis theorizes a syndrome whose features are discussed and motivated all along the case study, the syndrome has been baptized “Platania’s syndrome” and it’s complex relational model is hereby described.The syndrome development model covers only neurogenic consequences of Hypoglossal Nerve Neuropathy (HNN) but please note that there is evidence of Hypoglossal Rootlets Emergence Entrapment (HREE) inducing Vertebral Artery (VA) vessel sufferance and vascular insufficiency (conflict with Hypoglossal nerve), despite the potential high harmfulness of these findings they are not directly relatable to posture, as such, beyond the scope of the present analysis.
(click on the labels to navigate)
Dossier
Platania’s syndrome case elements collection grouped by classes:- Anamnesis: personal, familiar… and historical informations;
- Lamented symptoms: patient’s complaints;
- Resolution attempts: diagnostic and/or therapeutic intervention aimed at problem resolution
- Documentation: diagnostic lab exams or other evaluation report.
| DOSSIER: resolution attempts | |||
| List of all the therapeutic attempt in chronological order, along with the continuous enhancement of the diagnostic hypothesis through the whole exclusion process. | |||
| # | Attempt | Status | Outcome |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: unknown; Pathomechanical hypothesis: unknown; Etiological hypothesis: unknown |
||
| Dra01 | Chiropractic 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: hip torsion and thigh
anterior/posterior muscle unbalance Therapy: manipulation on the neck, spine, hip, sacroiliac and other techniques Outcome: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor
disorder; Pathomechanical hypothesis: generic muscle unbalance; Etiological hypothesis: neurological problem |
||
| Dra02 | Neurology 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: no |
| Dra03 | Applied kinesiology 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: yes Outcome: no |
| Dra04 | Osteopath 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: craniosacral therapy, manipulations Outcome: no |
| Dra05 | Osteopath 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: manipulations Outcome: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor disorder; Pathomechanical hypothesis: left psoas major (PM) weakness; Etiological hypothesis: radiculopaty, lower motor neuron disease; |
||
| Dra06 | Neuraltherapy 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: neuraltherapy on scars with emla procaine cream Outcome: no |
| Dra07 | Chiropractic 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: reactive food diet, neurolinfatic spots treatment, manipulations Outcome: no |
| Dra08 | Applied kinesiology 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: yes Outcome: no |
| Dra09 | Podiatrist: | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor disorder Pathomechanical hypothesis: left tibialis posterior (TP) weaknes; Etiological hypothesis: L5 radiculopaty, lower motor neuron disease; |
||
| Dra10 | Neurology 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: postural problem Therapy: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor
disorder; Pathomechanical hypothesis: left TP weakness; Etiological hypothesis: soleus accessorius, neurological teeth… |
||
| Dra11 | Self techniques | Completed |
Alexander: self awareness improvement, helpful
for self evaluation method, no postural benefit Feldenkrais: self awareness improvement, helpful for self evaluation method, no postural benefit |
| Dra12 | Acupuncture | Completed |
Diagnosis: chinese medicine
diagosis… Therapy: yes Outcome: no |
| Dra13 | Neuraltherapy 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: neuraltherapy on suspect dermatomes with procainum compositum intradermal injections Outcome: isolated regression event occurrence, not repeatable, suspected lucky coincidence |
| Dra14 | Shiatzu | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: yes Outcome: no |
| Dra15 | Neuraltherapy 3 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: neuraltherapy on suspect “neurological teeth” with procaine local anaesthesia Outcome: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor disorder; Pathomechanical hypothesis: left TP weakness; Etiological hypothesis: mercury induced neuropathy; |
||
| Dra16 | Dentist 1 | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: mercury amalgam removal therapy Outcome: suspect illness resistance improvement, nothing relevant to posture |
| Dra17 | Plantar reflexology | Completed |
Diagnosis: no Therapy: yes Outcome: no |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: left lower limb motor disorder; Pathomechanical hypothesis: left TP weakness; Etiological hypothesis: stomatognatic disorder; |
||
| Dra18 | Dentist 2 | Completed |
Diagnosis: postural disorder of stomatognatic
pathomechanics
Therapy: orthodontic + all wisdom teeth
extraction + parodontal complications therapy Outcome:
Complete discussion is available in orthodontic treatment section. |
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: current mechanical
hypothesis (see Mechanics); Pathomechanical hypothesis: swallowing defects (first primary) and stomatognatic disorder (second primary); Etiological hypothesis: swallowing habit; |
||
| Dra19 | Speech therapist | Interrupted |
Goal: working on tongue functionality to
somehow improving swallowing disorder and it’s stomatognatic
impact Diagnosis: no Therapy: tongue exercises Outcome:
|
| Diagnostic hypothesis |
Mechanical hypothesis: current mechanical
hypothesis (see Mechanics); Pathomechanical hypothesis: current pathomechanical hypothesis (see Pathomechanics); Etiological hypothesis: current etiological hypothesis (see Etiopathogenesis); |
||
| Dra20 | Neurology 3 | Interrupted | Diagnosis: investigation terminated due to insufficient of collaboration of health care professionals |
| Dra21 | Vascular surgery 1 | Interrupted |
Diagnosis: investigation terminated due to insufficient
of collaboration of health care professionals Details are available in DOSSIER:documentation under (Ddo09) |
| Dra22 | Auriculotherapy 1 | Completed |
Goal: acting on vagal and glossopharyngeal
reflexive points to hopefully have a feedback in afferences
sensitiveness Therapy: ear piercing appliance over vagal and glossopharyngeal reflexive points Outcome: cause-effect reaction but not repeatable:
|
| Dra100 | Pranotherapy | Interrupted |
Goal: testing the capability of this therapy to affect Vertebral Artery (VA) position Therapy: heands contact over the head and neck Outcome: none |
| Dra23 | Atlantotec 1 | Completed |
Goal: use the atlas transeverse process to somehow
move the Vertebral Artery (VA) away from it’s habitual position
in order to relieve pressure on the XII cranial nerve Diagnosis: atlas has been found, by palpation, to be right-rotated Therapy: deep sub occipital massages, after which, appliance of vibrating pressure (by means of a vibrating device) to reposition the atlas Outcome: cause-effect reaction but not repeatable
|
| DOSSIER: documentation | ||
| # | Exam | Report |
| Ddo01 | Lumbar spine RX | report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo02 | Left lower limb Electromyography (EMG) | no tibial nerve anomaly, report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo03 | Lumbar spine MRI | L3-L4 Hernia plus further degenerative processes, report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo04 | Gastroduodeno GDS | small hiatal hernia due to esophagus slip, report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo05 | Cranial RX | no anomaly, report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo06 | Dental panoramic RX | No anomaly except teeth crowding, report omitted… reserved information |
| Ddo07 | Cycling ergonomic analysis | left lower limb motor disorder |
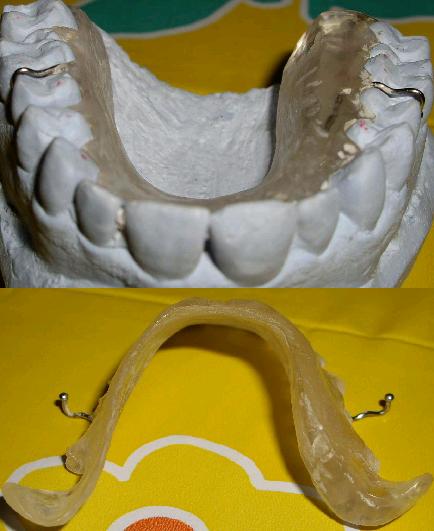
| Ddo07a | Custom designed oral splint implemented for differential diagnosis exclusion (Ptd03): by means of 2 asymmetric palatal sides, tongue is fit in a central position within palate, teeth are free to occlude, mastication and swallowing are preserved, phonation is normal, only tongue positioning is affected by this splint. | |
| Ddo08 | Carotid artery Doppler | No tortuosity, normal vascular flow |
| Ddo09 | MRI of intracranial and neck vessels; MRI of brain and brainstem |
Clue of left Vertebral Artery (VA) overlying
hypoglossal rootlets emergence, a neurovascular conflict lesion is further
confirmed by left VA branch decreased blood flow (Full Arrow). This hypothesis is described in the Etiopathogenesis and thoroughly discussed and validated in STAGE 4 discussion section. |
|
Coronal
view (Full Arrow = left VA branch, Arrow = right VA branch)
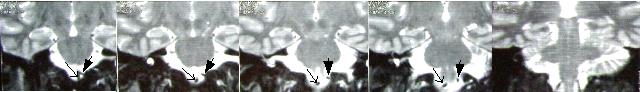 click to enlarge high resolution (1.2 Mb), 1 of 2 high resolution (1.1 Mb), 2 of 2 |
||
|
Top
view (Full Arrow = left VA branch, Arrow = right VA branch)
 click to enlarge high resolution (1.3 Mb) |
||
|
Sagittal
view (Full Arrow = left VA branch, Arrow = right VA branch)
 click to enlarge high resolution (1.1 Mb), 1 of 2 high resolution (1.1 Mb), 2 of 2 |
||
|
Vessels
view (Full Arrow = left VA branch, Arrow = right VA branch)
 click to enlarge high resolution (1.2 Mb), 1 of 2 high resolution (1.3 Mb), 2 of 2 |
||
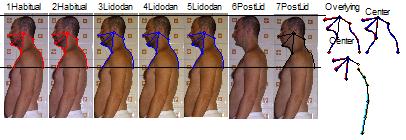
| Ddo10 | Vagal reset procedure: local appliance of 30mg of lidocaine 2% in the pharynx | Cause-effect repeatable reaction provides clue
of vagal afferences mediating head forwarding postural strategy (HFPS). Further discussion is available in vagal reset and Ere02 sections. |
| First
appliance: sudden index 0 regression event,
lasted for 2 hours, after which, spontaneously restore index
–2; |
||
| Second
appliance (after 4 days): sudden index 0 regression event,
lasted for 2 hours, after which, spontaneously restore index
–2; |
||
Other ways to induce the effect of vagal reset are:
|
Cause-effect repeatable reaction are provided by
|
|
| Ddo11 |
Needle Electrode EMG: differential
left-to-right electrical potential of all muscles involved in HFPS Description:
|
To be undertaken Electromyogram dump: Day1: ??/??/2008, Day2: ??/??/2008 Fill with electrodiagnostical values Weak left extrinsic tongue muscles:
Overall inhibited left to right unbalance: ?? |
| Ddo12 |
Photograph Imaging: reproducible imaging of the
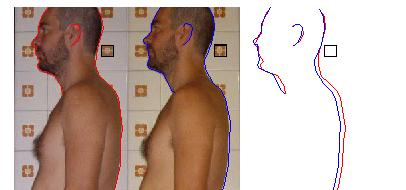
postural disorder Description:
|
To be undertaken Constants values:
To be filled with snapshots Day2: ??/??/2008 To be filled with snapshots |
|
Bugs report and technical issues notification to the webmaster are highly apreciated
|
| Posture, etiology of a syndrome - ©2008 Paolo Platania |